| Isotope | Atomic mass (Da) | Isotopic abundance (amount fraction) |
|---|---|---|
| 69Ga | 68.925 573(8) | 0.601 08(50) |
| 71Ga | 70.924 702(6) | 0.398 92(50) |
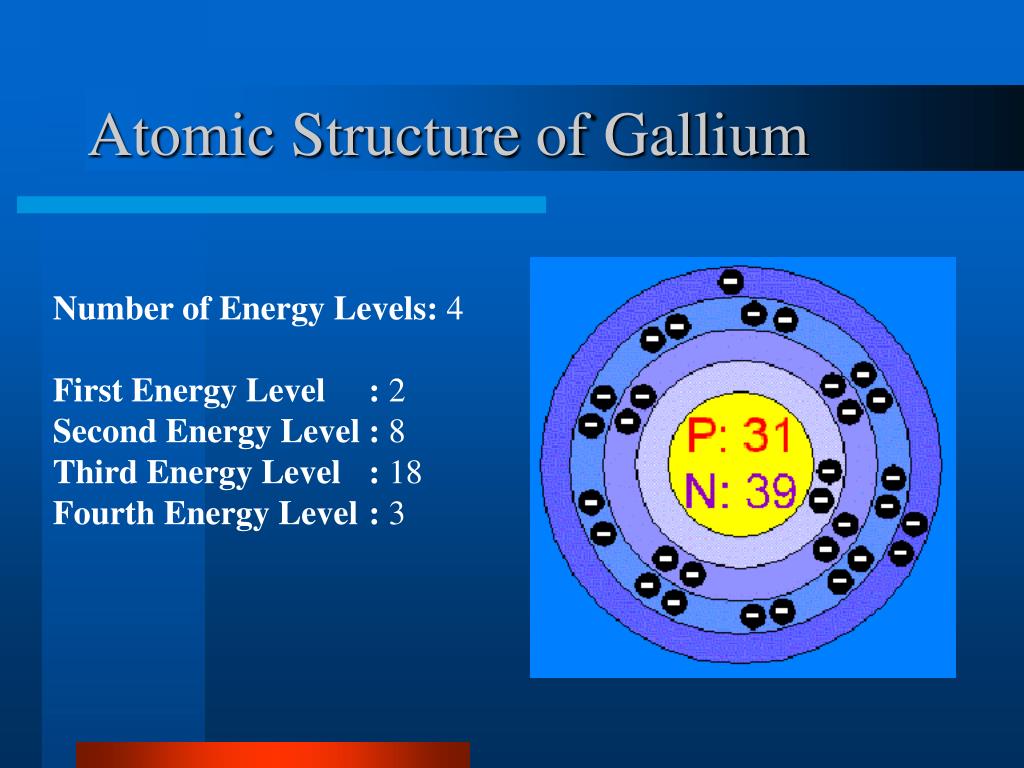
Gallium took the place of the placeholder element eka-aluminum. Gallium was first identified using spectroscopy by its distinct pair of violet spectral lines. Gallium's melting point (302.93 K) is low enough to melt the metal in the palm of your hand. Gallium is the element with the highest range of temperatures for its liquid phase. 32 Naturally occurring gallium is a mixture of isotopes that contains 60.11% Ga-69 (atomic mass = 68.93 u) and 39.89% of Ga-71 (atomic mass = 70.92 u). Which numerical setup can be used to determine the atomic mass of naturally occurring gallium? Recalculating the chemical ratios based on current values of the other atomic weights involved yields Ar (Ga) = 69.735, while the mass-spectrometric value with current atomic masses gives Ar (Ga) = 69.72. Furthermore, highly precise coulometric assay of Ga and As yielded Ar (Ga) = 69.737. Gallium has 31 known isotopes, ranging in mass number from 56 to 86. Only two isotopes are stable and occur naturally, gallium-69 and gallium-71. Gallium-69 is more abundant: it makes up about 60.1% of natural gallium, while gallium-71 makes up the remaining 39.9%. Gallium is also extracted from the flue dusts of coal. Isotopes: Gallium has 24 isotopes whose half-lives are known, with mass numbers 61 to 84. Of these, two are stable: 69 Ga and 71 Ga with natural abundances of 60.1% and 39.9% respectively.
Atomic Mass Of Gallium Oxide
In 1961, the Commission recommended Ar(Ga) = 69.72, based on the chemical ratio determinations as well as the isotope-abundance determinations. Recalculating the chemical ratios based on current values of the other atomic weights involved yields Ar(Ga) = 69.735, while the mass-spectrometric value with current atomicmasses gives Ar(Ga) = 69.72. Furthermore, highly precise coulometric assayof Ga and As yielded Ar(Ga) = 69.737. Meanwhile, new mass-spectrometricmeasurements confirmed the earlier mass-spectrometric values, yielding Ar(Ga) =69.724(2). Facing with this dataset, the Commission recommended an atomic weight of Ar(Ga) = 69.723(4) in 1983 favouring the mass-spectrometric data.
Significant variations occur in the n(69Ga)/n(71Ga) ratio of commercially high-purity Ga from different lots ofmaterial and different manufacturers, some exhibiting ratios 0.19 % higher and 0.12 % lower than thelaboratory reference material. Based on this information, in 1987 the Commission recommended Ar = 69.723(1), which has remainedunchanged since that time.
Purification of Ga by successive recrystallizations is accompaniedby small variations in isotopic composition, which measurably affect the triple-point temperature of gallium.
© IUPAC 2003
CIAAW
Gallium
Ar(Ga) = 69.723(1) since 1987
The name derives from the Latin gallia for France. It was discovered in zinc blende by the French chemist Paul-Emile Lecoq de Boisbaudran in1875. It was first isolated in 1878 by Lecoq de Boisbaudran and the French chemist Émile-Clément Jungflesch.
Atomic Mass Of Gallium 71
Isotopic reference materials of gallium.
